Sustainability Planning
Definition :
The sustainability planning is split in five steps:
Develop sustainability plans for the project,
Apply sustainability tools and metrics to project's cost/benefit assessment,
Create a materials filter for project materials selection,
Adhere to industry standards and sustainability design philosophies,
Qualify “make or buy” decisions with the latest sustainability tools and metrics.
1. Sustainability planning
Fundamental : Inputs needed to start the Sustainability planning
Sustainability management plan
Project scope statement
Planning documents
Enterprise environmental factors
Organizational process assets
Fundamental : Tools & techniques to achieve the Sustainability planning
Cost-benefit-analysis
Material composite analysis
Sustainability materials filter
Environmental assessment
Additional planning tools
Expert judgement
Fundamental : Outputs to close the Sustainability planning
Sustainability project plans
Sustainability metrics
Project document updates
Sustainability information management system updates
2. Tools and techniques to achieve the sustainability planning
To achieve the sustainability planning you have to answer the following question with using the following methods (Sustainability materials filter, Qualify “make or buy” decisions)
What Types of materials are used?
Poisonous or not
Grey list or black list or not
Virgin material or recyclable
How dependent are we on non-renewable resources for the procurement of raw materials, processing, manufacturing, logistics, etc ...?
Do any of our actions cause increased caution footprint, community displacement, community impact, or any other negative long-term impacts?
How the materials are being processed? Are they being processed in a way that is harmful to the community or to the environment?
First Set of Methods: Sustainability materials filter
Method : Environmental Impact Assessment
Environmental Impact Assessment
Greenhouse gases that require reduction:
Carbone dioxide (
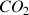 ),
),Methane,
Nitrous oxide,
Hydro-fluoro-carbons,
Sulphur hexafluoride.
Method : Method : The Melbourne Principles
The 6 Melbourne Principles (building):
P1: Provide a long term vision,
P2: Achieve long term economic and social security,
P3: Recognize the intrinsic value of biodiversity and natural ecosystems,
P4: Enable community to minimize thez ecological footprint,
P5: Build on the characteristics of ecosystems in the development,
P6: Recognize and build on the distinctive characteristics of cities including their human and cultural values.
Method : Method : A material filter
A material filter is a guide that outlines what materials, chemicals, and products are acceptable for use by the organization and business supply chain.
Black and grey lists are lists of banned or limited chemical or chemical compounds.
The project manager must be aware of these lists and any related chemical composition constraints on the project.
Second set of Methods: “make or buy” decisions with the latest sustainability tools and metrics
Method : "Fit to use" assessment
1- "Fit to use" assessment
To ensure that a product or system is build to do nothing more than what is required.
2- "Make or buy" assessment
Organization reassess their core business and decide to only build things that only align with their organizational goals and objectives.
3- Cradle to cradle planning
To plan and manage the transition of a products end-of-line.
An effective plan manages the dismantling and ultimate 100% reuse somewhere in the world.
4- ISO 14000
The ISO 14000 family provides information on environmental management.
5- Other tools
Expert judgement
Life cycle assessment
Life cost assessment (including indirect cost)






