What is sustainability in project management ?
Definition :
Sustainability in project management is defined by the “green project management”, part of the PMI (Project Management Institute) as follow : "Since the adoption of ISO 14001, which exists to help organization minimize how their operations impact the environment and comply with applicable laws, the subject of sustainability though project management had remained nebulous at best had been a lack of continuity among organization who desires to use project management as a mechanism to impart change"
Green project management
The issue developed by this definition is based on the low level of interest on this subject in academic literature. It is only a concept that must be developed.
To go further on this subject we suggest you to watch the following video.
You can watch some exemples.
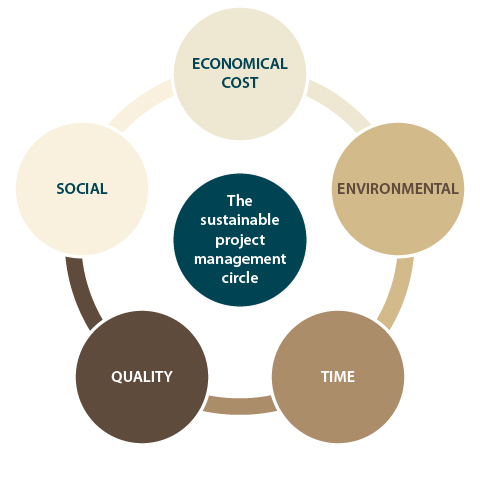
The Time / Cost /Quality and the TBL
Fundamental :
Sustainability in project management is about balancing or harmonizing social, environmental and economic interests in a project.
Developing Sustainability in Project Management takes into account the full life-cycle of the project / of the asset / of the product at hand.
Sustainability in project management is a way to cross the triple bottom line of business with the golden triangle of project
To go further on this subject we suggest you to watch the following video.
You can watch some exemples.
Sustainable Project Management
Fundamental :
The management of project-organized change
in policies, assets or organizations,
with consideration of the economical, social and environmental impact,
of the project, its result and its effect,
for now and future generations.
Example :
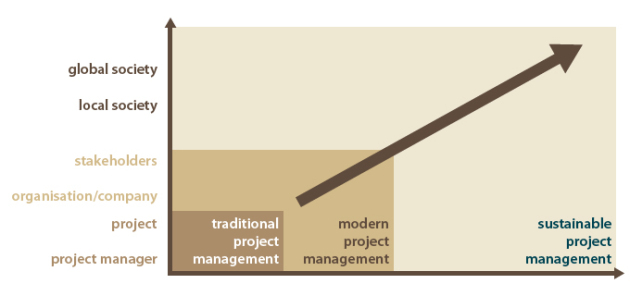
Sustainable development in project management can expand the perimeter of the project by increasing the temporal vision and his scope.
According with the following table, sustainable project management takes into account the societal impacts of the project and expands the definition of the perimeter of the project in two ways:
Local and global society (societal vision)
In time, incorporating the impact of the project on future generations
From: Sustainability in Project Management, By Gilbert Silvius, Ron Schipper, Julia Planko, Jasper van den Brink and Adri Köhler; Published May 2012; Paperback; ISBN 978-1-4094-3169-5
The following table explains the differences between a sustainable project approach and an orthodox project approach:
Sustainable Project Approach | Orthodox Project Approach |
|---|---|
Consensus | Top down decision-making |
Leaps of faith - climate change | Fact-based |
Systemic approach - ecosystem | Linear & mathematical analysis |
Social, environmental science | Engineering & Science |
Business judgement | Engineering judgement |
Business case (benefit) justification | Risked-based justification |
Design as a journey-with errors | Design as a deliverable-zero defects |
Triple bottom line | NPV |
Customer ownership | Outsourced |
Root cause | Specification |
Long term | Short term |






