Sustainability and organization
Fundamental : Impacts of industrial System on the environment
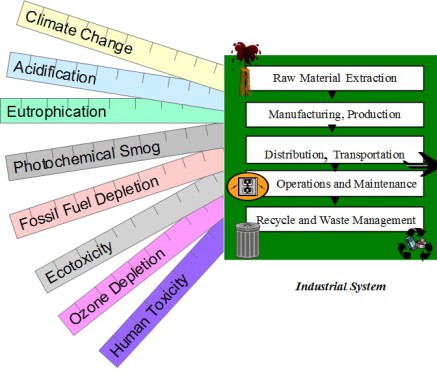
Any economic activity has an impact on the environment. The intensity of these impacts depends on the type of activity and the industrial system developed by the company.
Fundamental : Sustainability Considerations
All this impact of the economic activities on the environment could be integrate in four major considerations:
Ecological Consideration
Resource Use : Energy use, material intensity, water use, land use
Environmental Impact : GHG emissions, air emissions, solid waste, (pollutant effects)
Social Consideration
Health & Safety : Toxic reduction, hazards, process safety
Societal Impact : Workers' well-being, local community impacts/QOL, global societal impacts/contributions
Economy Consideration
Economic Impact : Financials along value-chain (corporate, customers, ...)
Business Perspective Consideration
Management : Internal process, value-chain partnership, stakeholder engagement
Alignment with business strategy, core values & competencies, market & regulatory drivers
Fundamental : What strategies
Constraints origin
Managers must increasingly integrate environmental constraints within the framework of their activities. These constraints are mainly due to:
International Organizations: OECD, UN, Global Impact, GRI,...
Authorities: a change in regulatory framework: Laws, standards ISO 14001 and SD 21000, REACH Directive,...
Shareholders and social rating
Customers, consumers : e.g. Nike
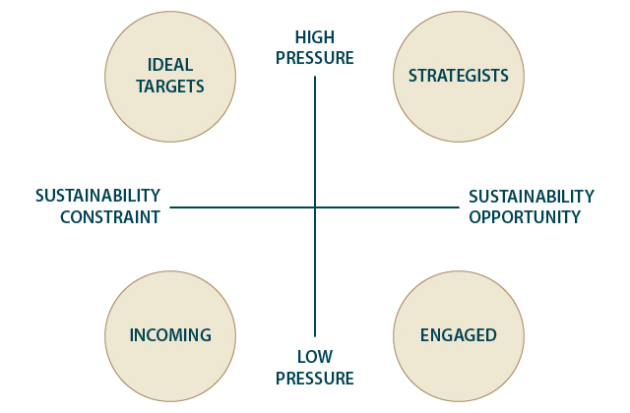
The following table shows the different ways for a manager to integrate the constraints of sustainable development. Two axes used to construct a typology of managers. The first takes into account the manager's vision for sustainable development: opportunity or constraint.
The second axis considers the weight of the constraint: high pressure or low pressure.