The sustainability components
The Triple P Concept of sustainability
Definition :
The phrase "the triple bottom line"
was first coined in 1994 by John Elkington. He highlighted that companies should be preparing three different bottom lines. One is the profit and loss account. The second is the bottom line of a company's "people account"
. The third is the bottom line of the company's "planet"
account.
The triple bottom line (TBL) consists of three Pillars: profit, people and planet. It aims to measure the financial, social and environmental performance of the corporation over a period of time.
People or Social développement
A business that wants to succeed sustainably must have a heightened commitment to providing products or services that comply with social norms and rules while contributing to an enhanced quality of life for all stakeholders.
Social approaches
Human approaches
Planet or environmental Development
A planet-focused business also identifies ways to mitigate some of the problems caused by past actions (climate change, pollution, overflowing landfills, and so on).
Environmental approaches
Ecological approaches
Profits or Economical développement
A company must generate profit and cash flow in order to remain solvent and continue its operations. Triple P strategy shows the deep interconnectedness of long-term profitability, strong relationships with people, and a commitment to improving the planet.
Economical approaches
Financial approaches
The Triple Bottom Line of Business
Definition :
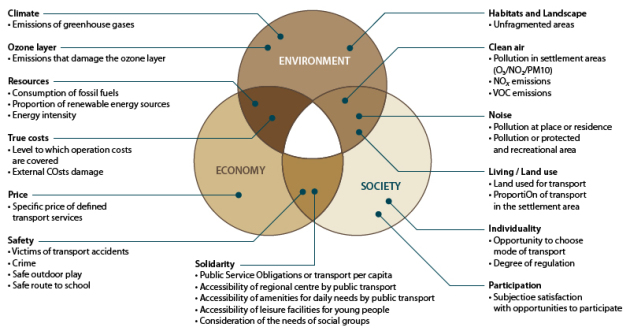
Very often, the Triple P concept of sustainability is known like the Triple Bottom Line of Business and is shown by the following scheme:
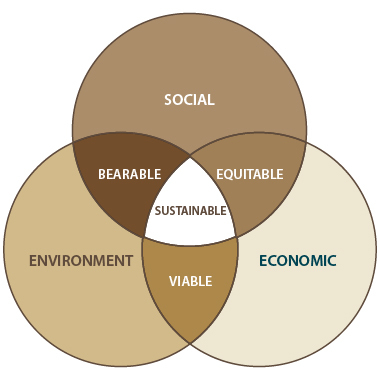
In this scheme, the crossover between the three spheres represents three types of development: bearable, equitable and viable development. The whole constitutes sustainable development.
The Triple consequences on sustainability concept
The TBL Business Case
The triple Bottom Line Case is a consequence of the crossover between the triple P and the triple bottom line of business. That affect cost, return on invest and value creation :
Short-term cost reduction
Energy efficiency and waste reduction
Longer-term return on investment
Investment in building improvements
Value creation
Existing markets
Value creation - New markets
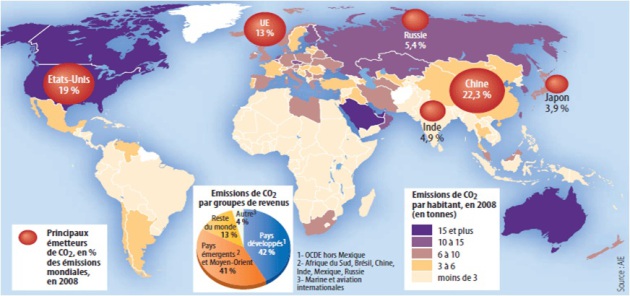
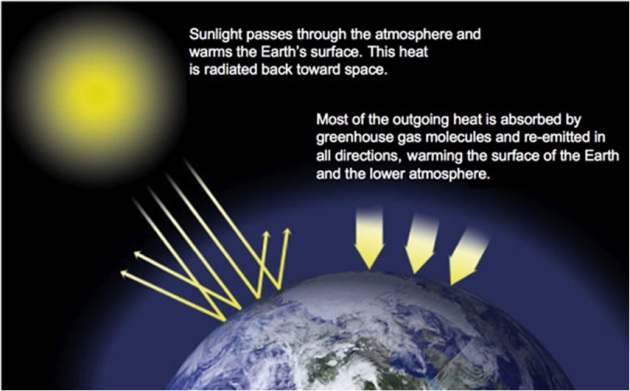
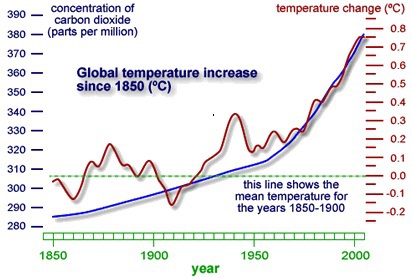
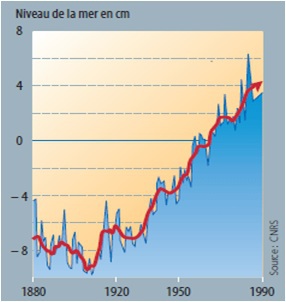
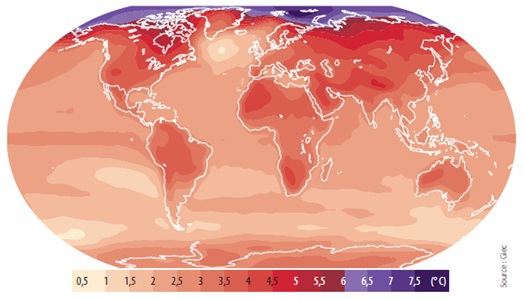
Example : Climate change
To go further on this subject we suggest you to watch the following video.
You can watch some exemples.
To go further on this subject we suggest you to watch the following video.
You can watch some exemples.
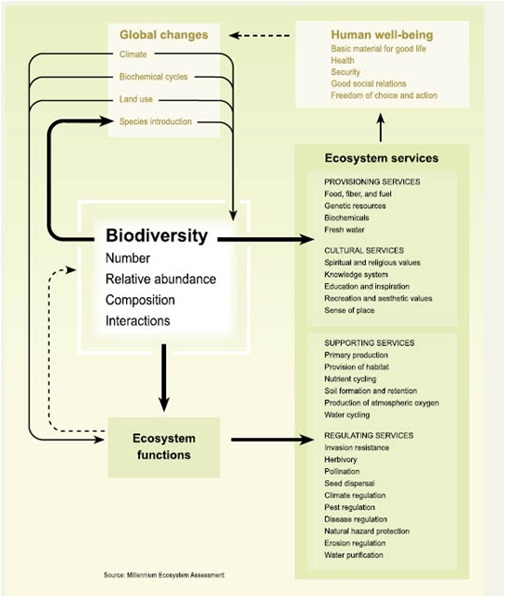
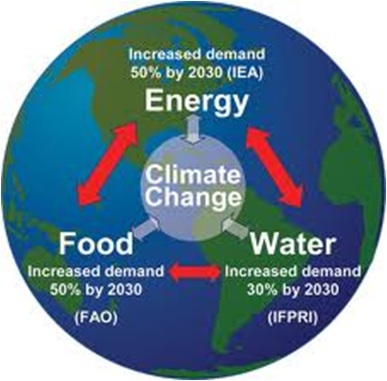
Example : Biodiversity
Global biological diversity is decreasing, due to direct and indirect human activity: hunting, loss of natural habitat (deforestation, desertification), etc.
To go further on this subject we suggest you to watch the following video.
You can watch some exemples.
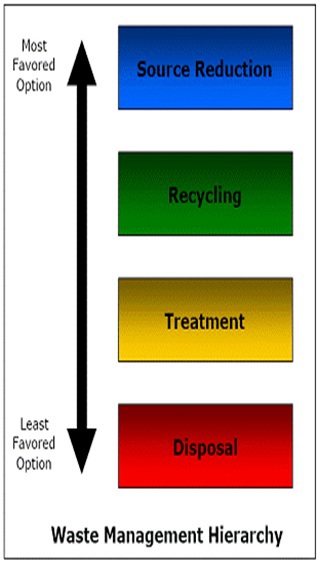
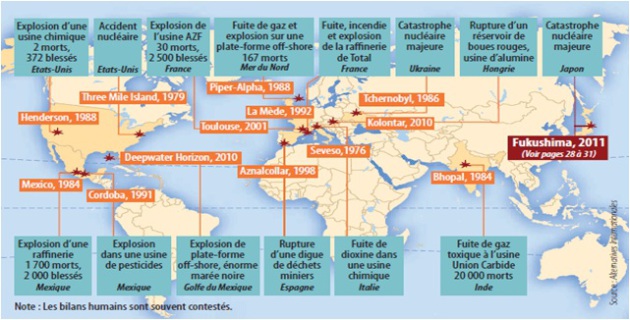
Example : Pollution and waste
To go further on this subject we suggest you to watch the following video.
You can watch some exemples.
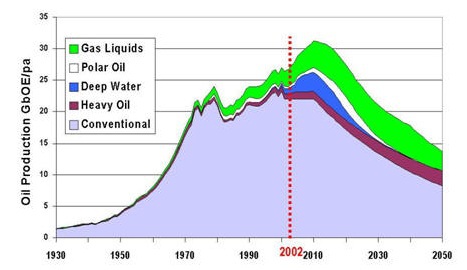
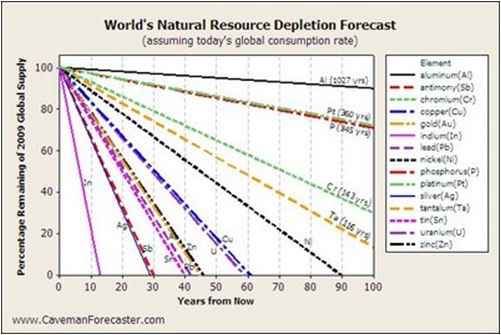
Example : Resources depletion
Resource depletion is an economic term referring to the exhaustion of raw materials within a region. Resources are commonly divided between renewable resources and non-renewable resources. Use of either of these forms of resources beyond their rate of replacement is considered to be resource depletion.
To go further on this subject we suggest you to watch the following video.
You can watch some exemples.